Thyroid Disease
 |
| Google images |
What is the thyroid?
 |
| Google images |
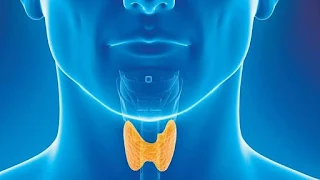
The thyroid may be a small organ that’s located within the front of the neck, wrapped round the windpipe (trachea). It’s shaped sort of a butterfly, smaller within the middle with two wide wings that reach round the side of your throat. The thyroid may be a gland. you've got glands throughout your body, where they create and release substances that help your body do a selected thing. Your thyroid makes hormones that help control many vital functions of your body.
When your thyroid doesn’t work properly, it can impact your entire body. If your body makes an excessive amount of hormone , you'll develop a condition called hyperthyroidism. If your body makes insufficient hormone , it’s called hypothyroidism. Both conditions are serious and wish to be treated by your healthcare provider.
What does the thyroid do?
Your thyroid has a crucial job to try to to within your body — releasing and controlling thyroid hormones that control metabolism. Metabolism may be a process where the food you're taking into your body is transformed into energy. This energy is employed throughout your entire body to stay many of your body’s systems working correctly. consider your metabolism as a generator. It takes in raw energy and uses it to power something bigger.
The thyroid controls your metabolism with a couple of specific hormones — T4 (thyroxine, contains four iodide atoms) and T3 (triiodothyronine, contains three iodide atoms). These two hormones are created by the thyroid and that they tell the body’s cells what proportion energy to use. When your thyroid works properly, it'll maintain the proper amount of hormones to stay your metabolism performing at the proper rate. because the hormones are used, the thyroid creates replacements.
This is all supervised by something called the pituitary . Located within the center of the skull, below your brain, the pituitary monitors and controls the quantity of thyroid hormones in your bloodstream. When the pituitary senses a scarcity of thyroid hormones or a high level of hormones in your body, it'll adjust the amounts with its own hormone. This hormone is named thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH). The TSH are going to be sent to the thyroid and it'll tell the thyroid what must be done to urge the body back to normal.
What is thyroid disease?
Thyroid disease may be a general term for a medical condition that keeps your thyroid from making the proper amount of hormones. Your thyroid typically makes hormones that keep your body functioning normally. When the thyroid makes an excessive amount of hormone , your body uses energy too quickly. this is often called hyperthyroidism. Using energy too quickly will do quite cause you to tired — it can make your heart beat faster, cause you to reduce without trying and even cause you to feel nervous. On the flip-side of this, your thyroid can make insufficient hormone . this is often called hypothyroidism. once you have insufficient hormone in your body, it can cause you to feel tired, you would possibly gain weight and you'll even be unable to tolerate cold temperatures.
These two main disorders are often caused by a spread of conditions. they will even be passed down through families (inherited).
Who is affected by thyroid disease?
Thyroid disease can affect anyone — men, women, infants, teenagers and therefore the elderly. It are often present at birth (typically hypothyroidism) and it can develop as you age (often after menopause in women).
Thyroid disease is extremely common, with an estimated 20 million people within the Unites States having some sort of thyroid disorder. a lady is about five to eight times more likely to be diagnosed with a thyroid condition than a person .
You may be at a better risk of developing a thyroid disease if you:
- Have a case history of thyroid disease.
- Have a medical condition (these can include pernicious anaemia , type 1 diabetes, primary adrenal insufficiency, lupus, atrophic arthritis , Sjögren’s syndrome and Turner syndrome).
- Take a medicine that’s high in iodine (amiodarone).
- Are older than 60, especially in women.
- Have had treatment for a past thyroid condition or cancer (thyroidectomy or radiation).
SYMPTOMS AND CAUSES
 |
| Google images |
What causes thyroid disease?
- Thyroiditis: This condition is an inflammation (swelling) of the thyroid . Thyroiditis can lower the quantity of hormones your thyroid produces.
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis: an easy disease, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis is an autoimmune condition where the body’s cells attack and damage the thyroid. this is often an inherited condition.
- Postpartum thyroiditis: This condition occurs in 5% to 9% of girls after childbirth. It’s usually a short lived condition.
- Iodine deficiency: Iodine is employed by the thyroid to supply hormones. An iodine deficiency is a problem that affects several million people round the world..
- A non-functioning thyroid gland: Sometimes, the thyroid doesn’t work correctly from birth. This affects about 1 in 4,000 newborns. If left untreated, the kid could have both physical and mental issues within the future. All newborns are given a screening biopsy within the hospital to see their thyroid function.
- Graves’ disease: during this condition the whole thyroid could be overactive and produce an excessive amount of hormone. This problem is additionally called diffuse toxic goiter (enlarged thyroid gland).
- Nodules: Hyperthyroidism are often caused by nodules that are overactive within the thyroid. one nodule is named toxic autonomously functioning thyroid nodule, while a gland with several nodules is named a toxic multi-nodular goiter.
- Thyroiditis: This disorder are often either painful or not felt in the least . In thyroiditis, the thyroid releases hormones that were stored there. this will last for a couple of weeks or months.
- Excessive iodine: once you have an excessive amount of iodine (the mineral that's wont to make thyroid hormones) in your body, the thyroid makes more thyroid hormones than it needs. Excessive iodine are often found in some medications (amiodarone, a heart medication) and cough syrups.
How is thyroid disease treated?
- Anti-thyroid drugs (methimazole and propylthioracil): These are medications that stop your thyroid from making hormones.
- Radioactive iodine: This treatment damages the cells of your thyroid, preventing it from making high levels of thyroid hormones.
- Beta blockers: These medications don’t change the quantity of hormones in your body, but they assist control your symptoms.
- Surgery: A more permanent sort of treatment, your healthcare provider may surgically remove your thyroid (thyroidectomy). this may stop it from creating hormones. However, you'll got to take thyroid replacement hormones for the remainder of your life.
Can I check my thyroid at home?
- Start by identifying where your thyroid is found . Generally, you’ll find the thyroid on the front of your neck, between your collar bone and Adam’s apple. In men, the Adam’s apple is far easier to ascertain . For women, it’s usually easiest to seem from the collar cram .
- Tip your head back while looking during a mirror. check out your neck and check out to hone in on the space you'll be looking once you begin the exam.
- Once you’re ready, take a drink of water while your head is tilted back. Watch your thyroid as you swallow. During this test, you’re trying to find lumps or bumps. you'll be ready to see them once you swallow the water.









0 Comments